Following steps showing you how to calibrate the PICkit 2:
1. Double click the shortcut of PICkit 2 on desktop as shown in figure 1
 2. PICkit 2 Programmer window show up (figure 2) and showing message “PICkit 2 not found. Check USB connections and use ToolsàCheck Communication to retry”
2. PICkit 2 Programmer window show up (figure 2) and showing message “PICkit 2 not found. Check USB connections and use ToolsàCheck Communication to retry” 3. Connect PICkit 2 with computer using appropriate USB cable, the power LED on PICkit 2 will lit as shown in figure 3.
3. Connect PICkit 2 with computer using appropriate USB cable, the power LED on PICkit 2 will lit as shown in figure 3. 4. Click Tools/Check Communication on PICkit 2 programmer windows, as shown in figure 4, the programmer will then show message “PICkit 2 found and connected”
4. Click Tools/Check Communication on PICkit 2 programmer windows, as shown in figure 4, the programmer will then show message “PICkit 2 found and connected” 5. Click Tools/Calibrate VDD & Set Unit ID, as shown in figure 5.
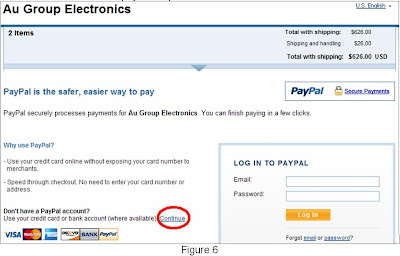
5. Click Tools/Calibrate VDD & Set Unit ID, as shown in figure 5. 6. “PICkit 2 VDD Calibration” window show up, click next to proceed (figure 6)
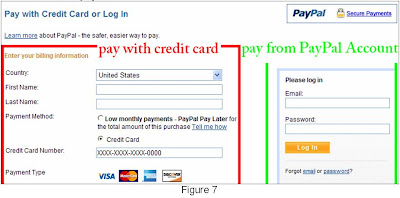
6. “PICkit 2 VDD Calibration” window show up, click next to proceed (figure 6)PICkit 2 VDD calibration window will show with the 3 steps (figure 7)
 Step 1. Make sure the PICkit 2 is not connected to any device or circuit board.
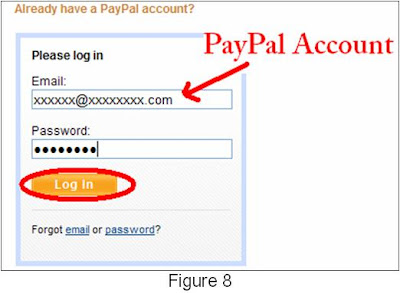
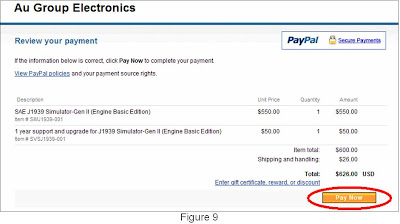
Step 1. Make sure the PICkit 2 is not connected to any device or circuit board.Step 2. Connect a voltage meter between pin 2 (VDD) and pin 3 (GND) of the CB0703 (PICkit 2) ICSP connector (the pin number is defined as shown in figure 8). The voltage meter showing at 0.2mV (figure 9).
 Step 3. Click NEXT and PICkit 2 will apply approximately 4 volts to the VDD pin.
Step 3. Click NEXT and PICkit 2 will apply approximately 4 volts to the VDD pin.Step 4. Connect a voltage meter between pin 2 (VDD) and pin 3 (GND) of the PICkit 2 ICSP connector again, the reading on the volt meter is the actual voltage measured on VDD (figure 10). Enter the value in the box as shown in figure11.
 Step 5. Click the CALIBRATE button to calibrate the PICkit 2. “CALIBRATION SUCCESSFUL” message displayed. Click “Next” to proceed (figure 12).
Step 5. Click the CALIBRATE button to calibrate the PICkit 2. “CALIBRATION SUCCESSFUL” message displayed. Click “Next” to proceed (figure 12). 7. “Unit Identification Name” window show up, type “MYPICKIT2” or any other name and click “Assign Unit ID” button, message “Unit ID Assigned to this PICkit 2” displayed. Click “Finished” button (figure 13).
7. “Unit Identification Name” window show up, type “MYPICKIT2” or any other name and click “Assign Unit ID” button, message “Unit ID Assigned to this PICkit 2” displayed. Click “Finished” button (figure 13).8. PICkit 2 Programmer – MYPICKIT 2 window show up, and a message “PICkit 2 connected. ID = MYPICKIT 2” display (figure 14).

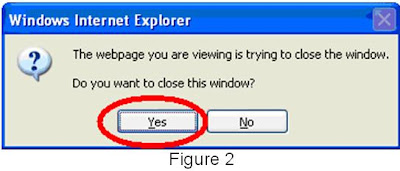
 2. Click “Continue Shopping” icon, as shown in figure 1, a question window may display (figure 2), click "Yes" to get back to original webpage for selecting other products
2. Click “Continue Shopping” icon, as shown in figure 1, a question window may display (figure 2), click "Yes" to get back to original webpage for selecting other products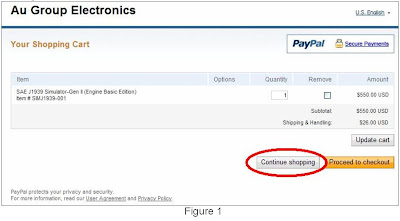
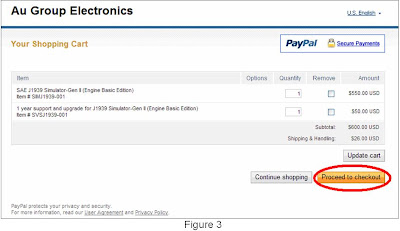

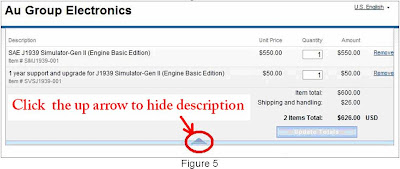



 Note: The last test value of VDD will affect the test result of PGC and PGD on step 6.
Note: The last test value of VDD will affect the test result of PGC and PGD on step 6.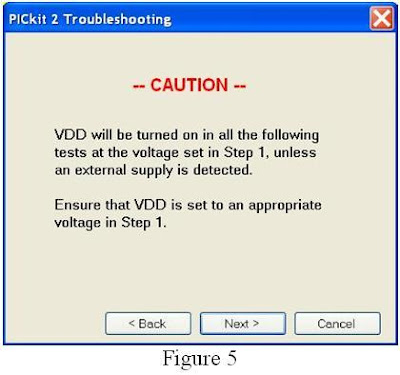
 5.Verify VPP
5.Verify VPP  5.2.Click "MCLR On" button, volt meter measures (Pin1 +, pin 3- ) at a few mV (Figure 8-1 shows 6.5 mV).
5.2.Click "MCLR On" button, volt meter measures (Pin1 +, pin 3- ) at a few mV (Figure 8-1 shows 6.5 mV). 6.Verify PGC + PGD
6.Verify PGC + PGD  6.2.Under PGD/ICSPDAT:
6.2.Under PGD/ICSPDAT:  6.3.Under PGC/ICSPCLK:
6.3.Under PGC/ICSPCLK: Note: these voltage values (figure 11-3 and 11-4) maybe different depends on the last test value of VDD (see step 4).
Note: these voltage values (figure 11-3 and 11-4) maybe different depends on the last test value of VDD (see step 4).




































